What is a monitor? A monitor is called a device through which users can communicate with the computer by receiving data.
It went through various stages from its birth, continuously evolving and offering new improvements, until it reached the modern led technology of today.
A computer is fundamentally a data processing center managed by a user; This relationship necessarily implies input and output of information, that is, interfaces, the monitor being a means of transmitting information assimilable by the user.
Before the monitor’s appearance, this communication was given through different lights and later through the teletype.
It was not until the 1970s that monitors as we conceive them now began to appear hand in hand with IBM’s innovative vision.
Thus, single color cathode ray tube monitors emerged, with the mere ability to display text, to later give way to monitors with color and the possibility of displaying graphics; Linked to these improvements, developed graphics cards capable of rendering graphics on the device, starting with CGA and going through EGA, VGA, and SVGA.
The monitors also varied in the possibility of size offered to the market and their aspect ratio. The size of a monitor is measured from one of its vertices to the opposite, and the aspect ratio accounts for the relationship between the height and the width of the monitor.
Another important point when considering a monitor is the maximum resolution they can offer and how it presents the sub-pixels.
In the latter case, should note that each pixel comprises three subpixels of three different colours: green, blue, and red; Depending on the monitor, these will be organized in different ways: triangles or lines.
In addition to pixels, other technical aspects to consider when talking about a monitor are response time or latency, which measures the time it takes for a pixel to go from an active state to an inactive one; the point size, which is nothing other than the space between two phosphors of a pixel and which accounts for the sharpness of the monitor; the functional area or area used for the image; the angle of view, or the angle from which can view the picture without blurring; and finally the luminance.
It is to be expected that monitors will continue to evolve in the future and show improvements that were unthinkable in the past due to the constant innovation process that we experience.
Table of Contents
What is a monitor characteristics?
All PC users use a monitor, also called, of course, a screen. But do you know what characteristics make a monitor?
The monitor has always been a fixture on PC users ‘ desks, from the bulky old cathode ray technology (CRT) monitors of yesteryear to the modern ones with micro-LED technology.
Thanks to the monitors, we can read news, play games or create programs, for example, and if we did not have a monitor or screen, interaction with a PC would be impossible since we would not know what we are doing.
We have in our hands one of the longest-lived peripherals in the history of the PC, and that is that without a monitor, we could not visualize any of the information we do on the PC.
Its definition is, effectively, a peripheral to visualize the data that a computer shows, or as its technical definition says, «a data output device».
Today, the PC monitor has many similarities with modern LCD televisions and, in fact, on these monitors you can perfectly watch TV over the Internet.
However, monitors tend to have certain characteristics that make them more suitable for the common tasks they usually perform, so not all screens are PC monitors.
What is a monitor characteristics to look for when buying a monitor?
The higher the monitor’s resolution, the better the visualization of the images you will have reflected; the resolution is measured in pixels.
A pixel is a tiny box or dot that contains an assigned colour. A pixel is part of an image.
Therefore, the images that we see reflected on the computer monitor daily are made up of millions of pixels (px).
They are so small that the human eye cannot detect them.
Another characteristic of the monitor is the number of inches that its diagonal contains. The more inches you have, the larger objects will be displayed, but size does not define how sharp the image is.
Remember that the sharpness will be given by the resolution of the pixels that each image contains.
The minimum number of inches recommended for a computer monitor is 15 inches.
But if it is your preference, there are larger 17, 19 or 21-inch computer monitors.
How does a monitor work?
The Computer Monitor is an output device through which pictures, texts and images are displayed in real-time, allowing programs to be executed.
The 21st century marks the splendour of the digital monitor age, the sophistication of software, hardware and communications. Computer monitors are not far behind.

It is very common to see monitors in almost every home; its main use is a peripheral device for computers. In most cases, all family members are familiar with this device.
Computers are electronic machines designed to store and process information, are the symbol of the digital revolution.
At present, the computer is used for various work and home branches for various purposes such as:
- Data storage
- Repetitive computations, data processing and calculations
- Drafting and transcription of documents
- Handling of machinery and other devices
- Video game
- Viewing images and videos
- One of the most relevant uses is using the computer as a communication channel through the web.
Now, the computer would not be such without its related devices, including the monitor.
The computer uses input and output devices for its operation, external parts or essential hardware for its correct operation, the most important being the computer monitor or screen.
Must connect the monitor for its respective operation to a computer. The computer is the medium that supplies the information reflected on the computer monitor screen.
The main work of the computer monitor is visualization; through this device, we can create, view or edit in real-time the orders that we issue to the computer or CPU.
Commonly, for the user to have greater comfort when using the computer monitor, he uses other hardware such as the keyboard and mouse or mouse.
Parts of a monitor
Generally speaking, a computer monitor is composed of:
- The casing: it is the external part that encloses the entire monitor. In LCD monitors, the most common colour is black. On CRT screens, they are commonly white.
- Data connector is the cable that goes from the computer monitor to the computer or CPU. Without it, it could display none of the images on the monitor. Some monitors dispense with the cable with Bluetooth technology.
- Button Panel: This is where the user can adjust the brightness and contrast of the screen. The position of the screen is also adjusted.
- Power button: is the most visible. It works to turn the monitor on and off. Commonly when pressed, it highlights in blue on the screen, indicating that the monitor is on.
- Electrical power supply: it is the cable that connects to the computer screen with electrical energy.
- The visualization instrument: it is the area where all the images and programs are displayed and observed.
- Support: Located at the bottom that keeps the monitor stable and secure.
Operation of a monitor
Depending on the type of computer, there are two types of monitors, Liquid crystal ( LCD ): flat screens and laptop screens, common computer desktop, based on the concept of the cathode ray tube. We will refer to the latter on this page.
In the Cathode Ray Tube, a beam of Electrons – which can precisely control in position and intensity – periodically stimulates a Screen internally coated with Phosphorus to make up the points that will make up the characters (letters, numbers and signs) on that monitor.
In color monitors, the screen is internally coated with a layer of red, green and blue tri-phosphor stimulated by three electron cannons (one for each color).
The images that are “painted” on the screen must be renewed so that they remain stable (without “flickering”), for which the electron beams must pass over the phosphorescent layer with a frequency greater than 65 Hertz (65 times per second).
This is called ” Refresh rate “, and it depends on the Graphics Card that we have installed on our computer.
What is a monitor main features?
Several features define what is a monitor looks like:
- Luminance: measured in cd/m² or Nits, it is a measure of the intensity of light emitted by the monitor. It is also known as “Brillo”.
- Color depth: measured in bits, it is the amount of color that the monitor can display.
- Color spectrum: these are the different color spaces for which these have been calibrated, such as sRGB or DCI-P3, to give a few examples.
- Aspect ratio: The ratio between the horizontal and vertical dimensions, such as 16: 9 (for every 16 pixels wide, there are nine high).
- Screen size: is the length (in inches) of the diagonal of the monitor screen.
- Screen resolution: the number of pixels on the screen, expressed as the product of the horizontal pixels multiplied by the vertical pixels, such as 1920 x 1080.
- Refresh rate: is the number of times the screen is refreshed per second and is measured in Hertz (Hz).
- Response time: the time it takes for a pixel to change from on to off and back on again. It is generally expressed in milliseconds (ms).
- Contrast ratio: The relationship between the highest brightness that a monitor is capable of generating with the darkest color that it can present.
- Delta-E: is the precision with which the monitor can represent a color. Generally, a Delta-E between 2 and 4 is a good precision, but below this, the human eye cannot perceive the difference.
- Viewing angle: is the angle measured in degrees, at which a user can see the monitor screen well without distorting the colors.
- Panel type: monitors use different types of panels, each with specific characteristics. They can be LED-IPS, LED-VA, LED-TN, etc.
- Pixel size: the size of a pixel represented on the screen.
- Video inputs: A monitor must have video inputs, ranging from the old-fashioned D-Sub (VGA) to DisplayPort or, on more ultra-modern monitors, the new USB-C cable standard.
Panels of a Monitor
To this day, all the panels that we are going to look at are LCD. Within this family, there are three main branches, and each of them has distinctive characteristics.
From TN, which is the oldest, to the modern IPS. Some are more suitable for editing work, general use models and others that are perfect for gaming.
As we already covered extensively in a previous article on this area, we are going to start by showing you a comparative table of the three types:
- TN (Twisted Neumatic)
- VA (Vertical Alignment)
- IPS (In-Plane Switching)
In turn, within the panels, we can find different types of lighting:
- Edge LED: the most widely used and also the cheapest. The light reaches the pixels from the edge through a diffuser panel.
- Full LED: all the LEDs on the screen are fully backlit.
- Local Dimming: the backlighting of the LEDs is dynamic and selectively fades or gains intensity to optimize contrast.
- OLED, AMOLED, and P-OLED: the so-called “organic” monitors. Pixels can be completely dynamically turned off to emphasize the effect and color achieved with Local Dimming technology. As a general rule, they are extremely expensive.
Resolution on monitor
Once we have decided on a type of panel, it is time to choose the resolution for our screen. As a general rule, the higher the resolution, the more image quality and the higher price.
We must also say that we don’t have to go crazy or obsess over a 4K monitor. In the same way as with the panels, the use that we are going to give it should be our priority.
Aspect ratio
Apart from screen resolutions, we also have their aspect ratio directly related to it. Currently, the number of standard formats has expanded, and the panoramic and ultra-wide models have become very popular, especially for curved monitors.
Currently, the “cinema” format that we know is 16: 9, and it is the most popular aspect ratio in monitors, but it has moved to 2.39: 1 more recently.
We show you a comparative graph based on Full HD so that you understand what we mean:
Given this, we establish the relationship between resolution and aspect of the most used resolutions:
- 720p is 16: 9
- 800p is 16:10
- 1080p is 16: 9
- 1200p is 16:10
- 2K is 16: 6
- 1440p is 16: 9
- 1600p 16:10
- 4K is 16: 9
- 8K is 16: 9
As you can see, the standard rotates between 16: 9 and 16:10, which does not mean that we cannot find wide formats such as 2560 × 1080 (2.37: 1) or 3440 × 1440 (32: 9).
In general, we can find wide or ultra-wide versions of all the resolutions mentioned above. This type of model has become very popular for the convenience of the on-screen workspace.
Still, these formats are not usually recommended for games, and it may be the case of playing dice with black stripes due to the lack of the existing resolution.
Color space
A domain that the ordinary user does not look at, or perhaps does not know how relevant it is.
Monitors in which the black is very pure while others have a grey tone? Blues that look like violets? These kinds of issues have to do with color space and are often the primary concern of graphic designers, illustrators, or video editors.
Of course, apart from our type of monitor, some programs and tools can help us calibrate its color, although obviously, it is only one more help. Let’s get to the topic:
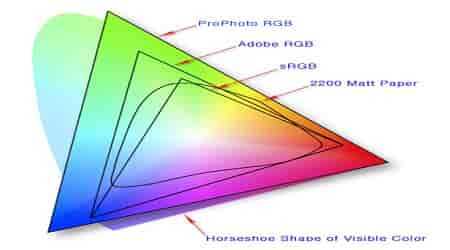
All monitors are handled in color spaces of the RGB model, and within these, there are those with wider ranges than others.
RGB refers to the three types of LEDs that create color mixes from Red (red), Green (green), and Blue (blue) in a process called Additive Synthesis. Within RGB, we can find variables, and these are responsible for the intensity or purity of its colors.
sRGB
Standard RGB is the original model and closest to the real color (based on cyan, magenta, yellow and black) or 2200, Matt Paper.
It is also the standard model for the internet and the vast majority of electronic devices since its color range is the smallest in the catalog.
Adobe RGB
Next in size. Created in 1998, this improved model expands the sRGB color catalog by up to 50%. By displaying a larger palette, it is an ideal color space for editing, illustration and design work.
In general, it is worked on both for images that will be used for web format and for printing, so it is later transferred to CMYK with better chromatic quality.
ProPhoto RGB
The ProPhoto RGB was introduced by Kodak in 2011 and is the latest on the list. Of all of them, it is the model with the widest register, standing out for including more colors than the human eye can perceive. This is because it is the closest to the more than 16 million existing RGB light colors .
This makes the images and video created with this spectrum very rich but difficult for editors to work with since, for us, at least 13% of this spectrum are “imaginary colors” since we cannot discern their tones.
2200 Matt Paper
The “matte paper” represents the physical color. This category is included to show the color restrictions subject to the CMYK ink printing process.
Color is light, and while on screens, we can generate around 16 million colors in physical materials, this is more difficult since it is impossible to generate the same volume of a variety of tones.
This is why we cannot expect the same contrast or vibrant tones in a physical format as we do on a monitor.
The color spectrum is greatly reduced, and this is why designers and illustrators worry so much about calibrating their screens in one go. not to distort the colors of the real finish compared to what they see on their monitors.
Color depth
Once we have dealt with color spaces, the question of color depth remains. It assumes the amount of color information that we can see in each pixel on the monitor.
This information is measured in Bits and on monitors. It usually ranges between 10 and 32 bits, depending on their age. We show you the equivalence:
- 1 Bit: 2 colors per pixel.
- 8 Bit: 256 colors per pixel.
- 10 Bits: 1024 colors per pixel.
- 16 Bit: 65,536 colors per pixel.
- 24 Bit: 16,777,216 colors per pixel.
- 32 Bit: 16,777,216 colors per pixel, and 256 more (8 Bit) added to the Alpha channel for an opacity factor.
Brightness and contrast on the monitor
Just as relevant as the color space and depth of the same are brightness and contrast. Let’s start by clarifying how each of them affects our monitor:
- Brightness: is the brightness emitted by the monitor. It is measured in candela per square meter (cd / M2) and can be judged by the quality of the screen display in bright or low light environments. Most monitors today have analogue calibratable brightness with a panel on the same screen.
- Contrast: this is the difference between the brightest pixel on the screen versus the darkest. There is no standard for contrast, but each brand establishes its ideal percentage based on production or quality controls. We can find it in two models: real contrast or dynamic contrast.
- True contrast: all pixels on the screen are lit, and pure dark is in those lit black. It is the original contrast, and its ideal ratio is around a ratio of no less than 1,000: 1.
- Dynamic contrast: In the darkest areas of the screen, pixels are dynamically turned off to generate more color depth. They greatly enrich the on-screen experience and can reach a contrast from 50,000: 1 to crazy 5,000,000: 1.
To reliably assess the brightness and contrast quality, the most efficient and practical way to do this is to reproduce a very dark video or image in a very bright environment.
If the quality that we perceive in this way is good, we can be sure that we can expect an ideal display in moderate light environments.
Response time
This is a section that interests the players much more and not without reason. It consists of the frequency with which they monitor and the computer exchange information.
When milliseconds are relevant in your life, you learn that the response time of your monitor can make a difference.
At the same time, for the general office automation user, it is irrelevant. The standard for current monitors is that the information displayed on the screen is processed in an average of 5ms (milliseconds), and from there, we can find monitors of 3ms, 2ms.
Refresh Rate (FPS) and Hertz
Frames Per Second (frames per second) are also a point to value on the monitors, and once again, it is the players who are most interested in this section.
FPS and Hz (hertz) are closely linked since hertz defines the maximum number of frames per second that our monitor can display. We can see 30 FPS on a 60 Hz monitor but not 80 FPS on the same monitor.
The norm is that today’s monitors operate at 60 Hz, so their refresh rate is 60 frames per second. These are the most popular and cheap models, and increasing the Hz increases the FPS and its price. All that said, the most popular models are:
- 60 Hz, up to 60 FPS.
- 120 Hz, up to 120 FPS.
- 144 Hz, up to 144 FPS.
- 180 Hz, up to 180 FPS.
- 240 Hz, up to 240 FPS.
Arrived here, it is necessary to make certain clarifications:
- Traditionally, the human eye can see up to 23 FPS, but that does not mean that we cannot notice a greater smoothness in the movements that we see on a screen at 60 or 144Hz. I Can See This, especially in high-resolution video games. Particle, volumetric or texture animations will appear more fluid with a higher refresh rate, and all movement, in general, is much smoother. These are the defects that many games try to nuance with effects such as Motion Blur or film grain.
- Another important aspect of dealing with is the prices, and that is that the rise in hertz causes them to increase a lot. If we also add a higher resolution and that the monitor is curved, the thing usually gets completely out of hand.
Monitor connections
A monitor, also called a computer screen, is an output peripheral that graphically displays the computer’s data or processed.
Monitors are connected to the computer through a graphics card, the most common connection systems being between the graphics card and the display device VGA, DVI, HDMI and DisplayPort.
When purchasing a monitor or graphics card, it is necessary to check that their interfaces are compatible.
Types of Monitor Connections
What is a monitor connections types? Monitor connections are the different methods and interfaces that allow the connection between the monitor and the computer for the correct on-screen display of what is happening on the computer.
Along with the keyboard and mouse, the monitor is one of the most important peripherals of a computer since, without it, it is impossible to work with the computer.
The task of the monitor connection is to connect the graphics card with the display device (monitor) using connectors and cables.
When buying a monitor or a graphics card, it is essential to check that the interfaces of both devices are compatible. In some cases, there are also adapters between interfaces of different types.
There is also the mini variant of the interface for almost all monitor connections, which follows a different construction design from the original, smaller in size.
Currently, there are different types of connection such as VGA, DVI, HDMI and DisplayPort, among others. Until recently, the functions offered by the classic VGA monitor connection were sufficient.
However, more modern versions, such as the DVI, HDMI or DisplayPort interfaces and their respective mini versions, transfer much more image and audio information from the computer to the monitor.

VGA
The VGA (Video Graphics Array) connection is the conventional connection type and the oldest of all, although it is still current and functional for most computers.
The VGA standard was developed by IBM and has been on the market since 1987. It offers a type of analogue connection, which only allows video transmission, making the audio connection through another interface necessary.
This type of connection is being a little sidelined before the arrival of new interfaces that allow a higher image resolution and can transmit audio in the same connection.
The typical graphic resolution of the VGA system is 640 × 480 pixels, which is why it is also called “VGA resolution”. There is also the mini variant of the VGA interface.
DVI
The DVI (Digital Visual Interface) connection is much more modern than its predecessor VGA since the data transmission is not done in an analogue but digital way, allowing a higher image quality.
This interface can transmit images in Full HD of 1920 × 1080 pixels, depending on the graphics card that the computer has.
Today, all modern TFT displays have a DVI connection, usually in addition to the VGA connection. The DVI connection is also available in mini DVI format.
The DVI connection exists in 3 versions, which differ at first glance in the number of contacts or pins:
- DVI-D: transmits digital-only.
- DVI-A: only transmits analogue.
- DVI-I: allows both digital and analogue.
HDMI
What is a monitor HDMI connection? The HDMI connection is a type of connection that is gaining more ground every day, being present in computers and a wide variety of electronic devices, allowing the connection.
Although HDMI (High Definition Multimedia Interface) did not begin as an interface for computers, it is already very common among modern computers.
This connection, like the DisplayPort, allows, in addition to transmitting high-resolution images, the transmission of high-quality audio.
HDMI also exists in the Mini HDMI variation, present in small devices such as tablets or digital cameras.
DisplayPort
DisplayPort is a port for graphics cards created by VESA and rival HDMI, which allows transferring high-resolution video and audio.
A DisplayPort monitor connection will enable you to connect multiple monitors simultaneously, but it can also transfer both image and audio signals and additional information, for example, for touch screens.
A reduced version of this connector called Mini DisplayPort is widely used for graphic cards with multiple simultaneous outputs.
USB ports
A nice detail to have on the monitor as another extra to which to connect accessories such as the mouse or keyboard. If they are also the most recent versions, we can count on a better data transmission speed.
3.5 jack for headphone and microphone
Another little extra to improve our quality of life, especially if our tower is under the table or the cable of our headphones are rather short.
That the same monitor includes audio input and output port is something very positive and, without a doubt, many will appreciate the detail.
Other aspects to consider
Once we have seen the most important factors for a monitor such as resolutions, aspect ratio, formats and response time, we can focus on others not so crucial but also relevant such as:
Monitor size
Something that can mislead the insiders is that the higher the resolution, the larger the screen can be. Inches are not everything.
This is generally true, but it does not mean that the same 27 ″ screen is 4K or Full HD. It is important to assess that the screen may be large, but its image quality is low, so it is important to assess whether both or only one of the aspects is relevant to us.
Read Here Also About: Best Portable Monitor for MacBook Pro.
If we want a monitor to be used at a certain distance, we will be more interested in the size than the resolution. On the other hand, if we like to watch movies or games in high definition, we are probably willing to sacrifice part of the screen size to exchange higher image quality.
Ergonomics
It is a commonly forgotten aspect. That can raise the screen, turned or tilted on its axis, and adjust it to our height or the height of our table and seat. Those looking for the possibility of anchoring the monitor to a wall will also appreciate that it has handles on its back.
Blue light filter
It is an aspect that we have become increasingly concerned about in recent years as we have become more aware of the adverse aspects that this lighting on monitors can have on our eyes and sleep rhythms. For this reason, many monitors include filters that reduce their presence.
Speakers
Let’s face it: everyone who can prefer to have a set of speakers instead of screens that include them. The sound quality that we can expect from the integrated speakers is usually not the most ideal, and they are also an addition that tends to raise the price.
On the other hand, those lacking space or who do not have sound as a priority can value a monitor that has them.
Classification according to monitor standards
What is a monitor classification? According to the value of the monitor, they can be divided into several sections. Such as LED monitor, LCD monitor, Plasma Screen Monitors, MDA monitor etc.
All have been evolving to offer greater benefits, definitions and improve the quality of the Images.
MDA monitors
Monitors MDA for its acronym in English “Monochrome Display Adapter” emerged in 1981. Along with the IBM CGA card. The MDAs, popularly known for Monochrome Monitors, only offered texts; they did not incorporate graphic modes.

This type of monitors was characterized by having a single mainly green colour. It created irritation in the eyes of its users.
Characteristics:
- No graphics mode.
- Resolution 720_350 pixels.
- Monochrome text support.
- It does not support graphics or colors.
- The graphics card has a 4 KB video memory.
- Supports underline, bold, italic, normal, invisibility for texts.
CGA monitor
The CGA monitors for its acronym in English “Color Graphics Adapter” or ” Graphics Adapter Color ” in Spanish. These types of monitors were marketed from 1981 when developed the first graphics card in conjunction with an IBM standard.

Despite the launch of this new monitor, PC buyers continued to opt for MDA monitors; both were launched on the market in the same year, with competition between them. CGA was the first to contain a graphic color system.
Characteristics
- Resolutions 160_200, 320 × 200, 640 × 200 pixels.
- Color chart support.
- Designed primarily for Computer games.
- The graphics card contained 16 KB of video memory.
EGA monitor
For its acronym in English, “Enhanced Graphics Adapter” is a standard developed by IBM to display graphics, created in 1984. This new monitor incorporated a greater breadth of colors and resolution.

EGA incorporated improvements over the previous CGA. Years later, it would also be replaced by a monitor with greater characteristics.
Characteristics:
- 640_350 pixel resolution.
- Support for 16 colors.
- The standard EGA graphics card carried 64 KB of video memory.
VGA monitor
The VGA monitors for its acronym in English, “Video Graphics Array”, was launched in 1987by IBM. Since the release of VGA monitors, older monitors were becoming obsolete.
The VGA incorporated mode 256 with high resolutions.

Due to the development reached to date, included in the Graphic Cards, the previous monitors are not compatible with VGA; they incorporate analog signals.
Characteristics:
- Support 720 × 400 pixels in text mode.
- Support 640 × 480 pixels in graphic mode with 16 colors.
- 320 × 200 pixel support in graphics mode with 256 colors.
- Standard VGA graphics cards incorporated 256 KB of video memory.
SVGA monitor
SVGA, called by its acronym in English “Super Video Graphics Array”, also known as “Super VGA”, developed These monitoring types and standards were to eliminate incompatibilities and create new enhancements to its VGA predecessor.

SVGA was released in 1989, designed to provide higher resolutions than VGA. This standard has several versions, which support different resolutions.
Characteristics:
- 800 × 600 resolution, 1024_768 pixels and higher.
- For this new monitor, different graphics cards were developed, such as ATI, GeForce, NVIDIA, among others.
Monitor history
What is a monitor history? Created The first computer was in 1936, and its creator was Honrad Zuse. Therefore, it was the beginning of the computer monitor or monitors for pc.
However, the creator of the monitor was William Crookes in 1878. Little by little and over the years, each computer had a special card that achieved the induction of different programs that gave better use to the pc.
Later, in the 1950s, the teletypewriter was created, which promoted computer communication by logging in and passing data. In the 70s, the movement of CRT monitors began, which lacked colour, which is why they were called monochromatic.
However, despite all the innovations, the monitor’s function remained the same, only that people began to use it for different purposes that changed to the mute.
The monitor is basically monitoring
The term monitor can be used as monitoring. Because the information is collected, the collected information is monitored, studied and then it can follow through the monitor to a specific program or a specific event.

Road monitoring
The road monitor provides live information on weather and traffic conditions; its purpose is to provide efficiency in the traffic sector; it also gives users a simple way to know if there is traffic in the area where they are and find other ways that can help them to mobilize.
Medical monitoring
These are devices that monitor a disease or parameters for an estimated period; thus, it is possible to know in time if there is an emergency problem in which medical intervention is needed.
- Fetal monitoring: generally, in the last trimester of fetal pregnancy, monitoring is needed to know the heart rate of the fetus and other situations that may present before, during and after delivery.
- Monitoring vital signs: vital monitor signs are simply a device that detects and processes the parameters that the patient has a physiological level and has several alarms that call the attention of medical personnel to act immediately.
- Arterial monitoring: it is ABPM, better known as ambulatory blood pressure monitoring, it is a type of blood pressure monitor through which blood pressure results are obtained, this process must be carried out within the first 24 hours of alterations, and they should be accounted for to see if there are improvements.
Baby monitoring
These devices serve to keep an eye on the baby when he is asleep in his room or anywhere in the house. They serve as a method of supervision when parents are busy or absent.
Not all monitors are computer monitors
What differentiates a computer monitor from a TV, for example, is that the television is designed to receive the signal from the antenna and does not necessarily have to have video inputs.
Of course, its panel and its features are optimized for viewing television content, and for that reason, if you connect a computer to a TV, many times everything will be “weird”, even blurry.
On the contrary, a computer monitor does not have an antenna input (although some may have it, it is not normal), and instead, it does have one or more video inputs, such as D-Sub (VGA), DVI, HDMI, DisplayPort or USB-C.
Another difference is that all TVs have built-in speakers, while in the case of computer monitors, only some do (it is optional and depends on the manufacturer).
As for the screens that laptops have, they work slightly differently (and therefore, no one calls them “monitors”) since they are integrated into the computer.
They do not have video inputs or outputs since they are connected directly to the laptop’s motherboard, although it can have video outputs to connect, precisely, external monitors.
Your tablet can also be a monitor
You can also turn your tablet into a monitor, either through streaming or by connecting it to video output; for this, it is necessary to use special applications, but if you need a small additional screen for your configuration, then a tablet can be very good for you. Certain applications.
What are the uses and importance of monitors?
We can talk about the program to use for writing, the workflow, the schedule, the right place and the light, whether or not to play background music and a host of other choices that each one considers essential to enhance the arrival of the muses.
But today, taking advantage of the experience of so many years as a photographer and retoucher, I will talk about the monitor.
This guy is crazy; more than one will think, what does the computer monitor (or computer) matter at the time of writing?
Well, I’m sorry to disappoint those of you who think so, since the monitor is the equivalent of the pencil (pen or ballpoint pen) and paper used in the past.
Would you write the same with a broken pencil or pen on dirty and wrinkled paper with a Staedtler fountain pen or fine point lettering on heavy paper?
How many hours do you spend in front of the monitor writing, reviewing and correcting? Let’s not say the ones you spend watching videos, on social networks, advertising, etc.
You should then look for one that does not tire your eyes (or reduces that fatigue to a minimum) and shows the greatest possible sharpness.
Can you imagine that you were aware that you had several diopters in your sight but did not wear glasses to write? Well, it is the same. I have astigmatism and farsightedness (several diopters in each eye).
I tell you, I have three computers: a tower with Windows and a professional 27-inch photo retouching monitor with 2.5K resolution, a 13-inch Macbook Pro and a 15-inch Macbook Pro with a retina display. Now I detail the experience with each one.
Daily use, of course, the Macbook Pro 15-inch retina for writing, is the newest and with the best quality, speed and reliability. Due to various circumstances, the problem appears when I have to write or review with the 13-inch non-retina or, in my study, with the 27-inch monitor.
Without sounding exaggerated, because it is not at all, the feeling is like not wearing glasses, since I go from seeing each letter (even if the text is not greatly enlarged) as if it were printed on paper, to seeing it pixelated, no definition.
If we add that the brightness, contrast and uniform distribution of light on each screen point, I notice a huge difference between one monitor and another.
Maybe you think that you have spent your whole life with your monitor or your laptop and you manage well, that you do not need anything else,
The experience with my monitors at the time of writing has led monitor me to write this article and recommend those who dedicate several hours to writing (and can afford it financially) to use a monitor according to what the job demands.
A laptop with a retina screen is not cheap, and neither is a 4k or 5k monitor, but it pays off in health and performance with a single novel, let alone ten or more jobs.
Do not spend more money than is strictly necessary since the benefits of a retina laptop are far above those required by a word processor, but look for a monitor with 4k resolution in the minimum space (20-24 inches) and connect to him your tower or laptop.
What features should the best monitor have?
For us to have good visual performance, the best monitor must meet the following characteristics:
- Screen size: 15 inches is the recommended minimum tube size since, indeed, the video card and the operating system that we will use will be of the latest generation. But if you are going to run graphic or technical design programs, the recommended is 17, 19 or 21 inches.
- Type of tube: depending on the manufacturers, we can find Trinitron tubes (exclusive to Sony ) or “shadow mask” tubes, the most common.
- Resolution: it must be according to the task to be carried out, considering that a standard 640×480 VGA monitor will have images of lower quality and quantity of colours than a 1024×768 SuperVGA monitor.
- Frequency: greater than 65 Hertz
- Dot Pitch or dot size: 0.28 mm. or less.
How do you know if your monitor isn’t working?
When a computer fails to display its output to a monitor connected to it, there are two possible causes: the monitor or its cable is failing.
The computer’s video display subsystem is failing. Both problems can happen at the same time.
Unfortunately, monitors typically do not display their status information on the computer, so the software cannot diagnose your condition with certainty.
However, you can find out if your computer monitor is not working well by changing components.
Step 1
Turn off and then unplug the monitor that is currently connected to your computer.
Step 2
Connect the same monitor to a computer that you know is working properly. The computer must be on. If you get a good image on the screen, your original computer faults its video display subsystem.
Step 3
Connect a monitor that you know works well to the original computer. Turn on the monitor. If you see a good image on the screen, then your original monitor, or its cables and/or adapters, is the one with a fault.
Conclusions for the ideal monitor
We can all find our perfect screen according to the use we want to give it. In conclusion and after having gone through all the points of this tutorial, we present the most relevant things to take into account according to your needs:
Gaming monitor
In gaming, it is interesting to take into account:
- The screen: generally flat. If it is curved, in any case, 1800R.
- Response time: 1ms is ideal, but up to 3ms is also acceptable.
- Resolution: between 1080 and 2K is the most common in 144Hz monitors.
- VA type LCD panel: longer response time than TN panel but the better refresh rate.
- Refresh rate: at a professional level, the most used monitors are 144Hz.
Monitor for illustration, design and editing
For graphic works, animation, 3D or similar, we must look at:
- The screen does not matter so much if it is flat or curved, but it is recommended that it be made of IPS panels since they offer the best colors and contrast.
- Resolution: it is advisable to move from 1080p upwards, and in general, a good size monitor will be appreciated by many given the larger workspace.
- Brightness and contrast: just like color, they are critical factors, especially contrast. That around 1,000: 1 would be ideal.
- Refresh rate and response time: in general, these are not highly relevant factors since those above tend to matter more. With 60Hz and 5ms response, it can work correctly.
General-purpose monitor
A general-purpose monitor can exist in two variants: office automation and casual gaming or office automation and editing work.
We can find more basic models for these cases and try to combine the values mentioned in the two previous sections according to our priorities.
We hope that this article has been enlightening and useful in your adventure when documenting yourself to choose the monitor you need. Any questions, do not stop writing them in our comments section. Until next time!
Frequently Asked Questions about Monitor
What is a monitor?
It is a special device that performs different functions.
What is the monitor for?
To display charts or traces.
What is monitoring?
It is to carry out a special follow-up to a patient, person, situation, etc.
Who Invented the Computer Monitor?
According to studies, it was William Crookes in 1878, however, the tests were carried out thanks to Karl Ferdinand in 1897.
What material is the computer monitor made of?
Lead, phosphor, metal, plastic … Although each material varies according to the type of monitor.
Click here for details about: Wimaxit Portable Touch Monitor Review

